
What is Bitcoin?
A Beginner's Guide to Digital Currency
Bitcoin is the world's first decentralized digital currency, created in 2009 by an anonymous person or group using the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto. Unlike traditional currencies issued by governments (like the US dollar or euro), Bitcoin operates on a peer-to-peer network without the need for banks or central authorities.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll break down everything you need to know about Bitcoin, from how it works to how you can buy and use it safely.
Understanding Bitcoin: The Basics
At its core, Bitcoin is both a digital currency and a revolutionary technology. Think of it as internet money that you can send to anyone, anywhere in the world, without going through a bank.
Key Features of Bitcoin
- Decentralized: No single entity controls Bitcoin. It runs on a network of thousands of computers worldwide.
- Limited Supply: Only 21 million bitcoins will ever exist, making it scarce like gold.
- Transparent: All transactions are recorded on a public ledger called the blockchain, which anyone can view.
- Pseudonymous: You don't need to provide personal information to use Bitcoin, though transactions are traceable.
- Irreversible: Once a Bitcoin transaction is confirmed, it cannot be reversed or canceled.
How Does Bitcoin Work?
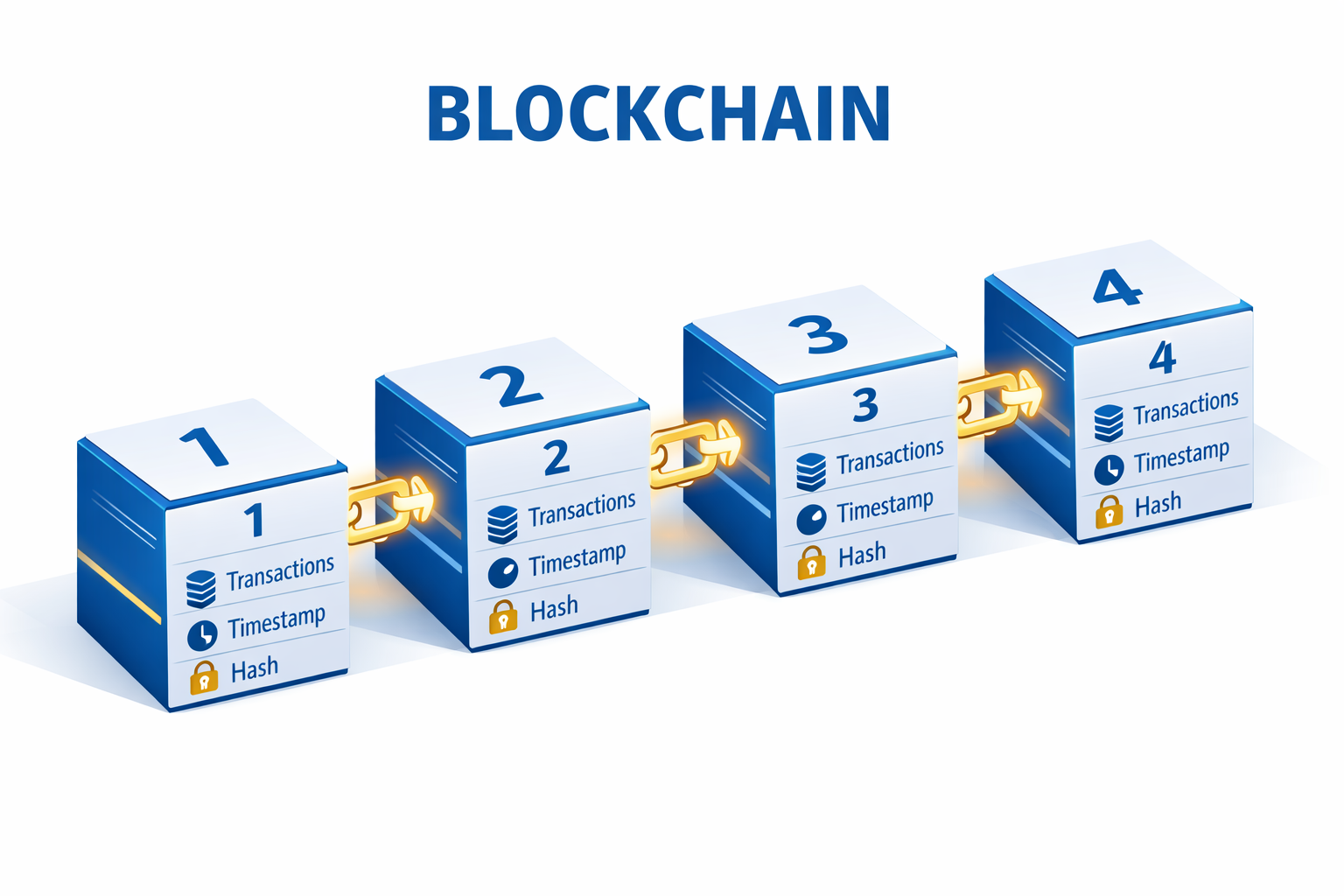
Bitcoin operates on blockchain technology, which is essentially a digital ledger that records all transactions across a network of computers. Here's a simplified breakdown:
The Blockchain Explained
Imagine a giant spreadsheet that everyone can see, but no one can cheat. That's the blockchain. Every time someone sends Bitcoin, that transaction gets grouped with others into a "block." These blocks are then linked together in chronological order, forming a chain—hence, blockchain.
Mining: Creating New Bitcoins
Bitcoin mining is the process by which new bitcoins are created and transactions are verified. Miners use powerful computers to solve complex mathematical puzzles. When they solve a puzzle, they:
- Verify and add new transactions to the blockchain
- Receive newly created bitcoins as a reward (currently 3.125 BTC per block)
- Collect transaction fees from users
This process occurs approximately every 10 minutes and is what keeps the Bitcoin network secure and functioning.
Why Was Bitcoin Created?
Bitcoin emerged in 2009, shortly after the 2008 financial crisis. Its creator, Satoshi Nakamoto, envisioned a currency that:
- Operates independently of governments and banks
- Cannot be inflated by printing more money
- Allows people to control their own money
- Enables fast, low-cost international transfers
The original Bitcoin whitepaper, titled "Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System," outlined a vision for financial freedom and privacy in the digital age.
How to Buy and Store Bitcoin
Step 1: Choose a Cryptocurrency Exchange
The easiest way to buy Bitcoin is through a cryptocurrency exchange. Popular options include:
- Coinbase: User-friendly, great for beginners
- Binance: Lower fees, more advanced features
- Kraken: Strong security, established platform
- Gemini: Regulated in the US, trusted by institutions
Step 2: Complete Identity Verification (KYC)
Most exchanges require you to verify your identity by providing government-issued ID and proof of address. This process, known as Know Your Customer (KYC), is required by law in most countries to prevent money laundering.
Step 3: Fund Your Account
You can typically fund your account via bank transfer, credit card, or debit card. Bank transfers usually have lower fees but take longer, while card purchases are instant but cost more.
Step 4: Buy Bitcoin
Once funded, you can buy Bitcoin directly on the exchange. You can purchase any amount—you don't need to buy a whole bitcoin. Bitcoin is divisible to eight decimal places, with the smallest unit called a "satoshi" (0.00000001 BTC).
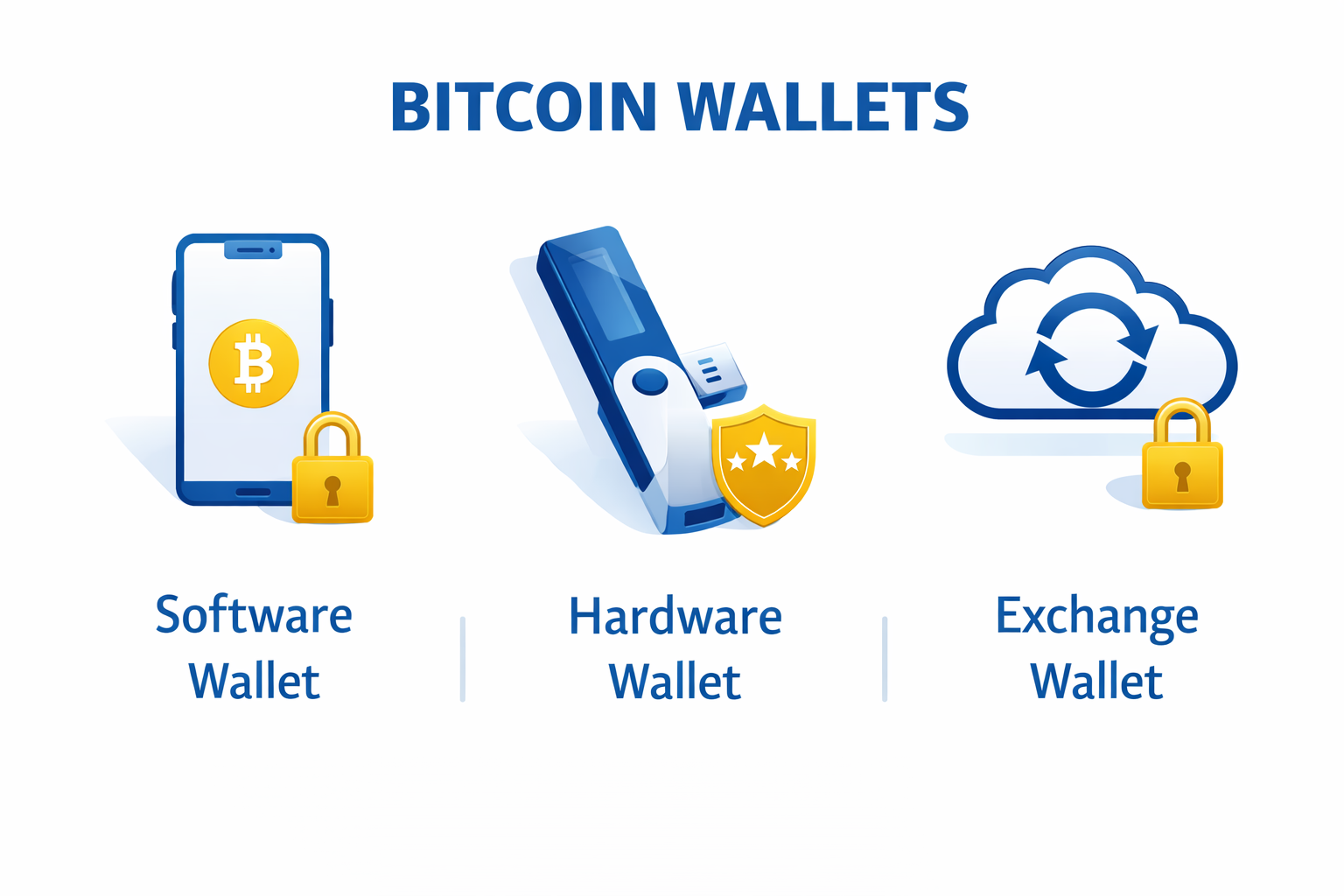
Step 5: Store Your Bitcoin Safely
You have several options for storing Bitcoin:
- Exchange Wallet: Keep it on the exchange (convenient but less secure)
- Software Wallet: Download a wallet app to your phone or computer (moderate security)
- Hardware Wallet: Physical device that stores your Bitcoin offline (most secure, recommended for large amounts)
Important: If you lose access to your wallet's private keys or recovery phrase, you lose your Bitcoin forever. Always back up your recovery phrase and store it securely.
Bitcoin vs. Traditional Money
Feature | Bitcoin | Traditional Currency |
Control | Decentralized | Centralized (banks/government) |
Supply | Fixed (21 million) | Unlimited (can be printed) |
Transactions | Peer-to-peer | Through intermediaries |
Speed | 10-60 minutes | Instant to 3-5 business days |
Fees | Variable (network-based) | Fixed by institution |
Privacy | Pseudonymous | Requires identity |
Common Bitcoin Myths Debunked
Myth 1: Bitcoin is Only Used for Illegal Activities
Reality: While Bitcoin was initially popular on dark web markets, the vast majority of Bitcoin transactions today are legitimate. Major companies like Microsoft, Tesla, and PayPal accept Bitcoin, and institutional investors hold billions in BTC.
Myth 2: Bitcoin is Too Volatile to Be Useful
Reality: Bitcoin's price can be volatile, especially in the short term. However, over the long term, it has generally trended upward. Many people use Bitcoin as a store of value (like digital gold) rather than for daily purchases.
Myth 3: Bitcoin Can Be Hacked
Reality: The Bitcoin network itself has never been hacked. However, exchanges and individual wallets can be compromised if proper security measures aren't followed. This is why it's crucial to use strong passwords, enable two-factor authentication, and store large amounts in hardware wallets.
Myth 4: You Need to Buy a Whole Bitcoin
Reality: Bitcoin is divisible into 100 million units called satoshis. You can buy as little as $10 worth of Bitcoin on most exchanges.
Risks and Considerations
Before investing in Bitcoin, it's important to understand the risks:
- Price Volatility: Bitcoin's price can swing dramatically in short periods. Only invest what you can afford to lose.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: Governments worldwide are still figuring out how to regulate cryptocurrencies, which could impact Bitcoin's value and legality.
- Security Risks: If you lose your private keys or recovery phrase, your Bitcoin is gone forever. There's no customer service to call.
- Scams: The crypto space has its share of scams. Be wary of "get rich quick" schemes and always verify information from multiple sources.
- Environmental Concerns: Bitcoin mining consumes significant energy, though an increasing percentage comes from renewable sources.
The Future of Bitcoin
Bitcoin's future remains both exciting and uncertain. Current trends and developments include:
- Institutional Adoption: Major financial institutions, including BlackRock and Fidelity, now offer Bitcoin investment products.
- Lightning Network: A second-layer solution enabling faster, cheaper Bitcoin transactions for everyday purchases.
- Global Remittances: Bitcoin is increasingly used for cross-border money transfers, especially in countries with unstable currencies.
- Store of Value: Many investors view Bitcoin as "digital gold"—a hedge against inflation and economic uncertainty.
Getting Started: Your Next Steps
If you're ready to explore Bitcoin, here's a simple roadmap:
- Educate yourself: Read the original Bitcoin whitepaper and follow reputable crypto news sources.
- Start small: Buy a small amount on a reputable exchange to get comfortable with the process.
- Secure your holdings: Learn about wallet security and consider a hardware wallet for larger amounts.
- Stay informed: Follow market trends, regulatory developments, and technological improvements.
- Never invest more than you can afford to lose: Cryptocurrency is still a relatively new and risky asset class.
Bitcoin represents a fundamental shift in how we think about money and financial systems. Whether it becomes the currency of the future or remains a niche investment, understanding Bitcoin is becoming increasingly important in our digital world.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute financial advice. Cryptocurrency investments carry risk. Always do your own research. See our Financial Disclaimer for details.